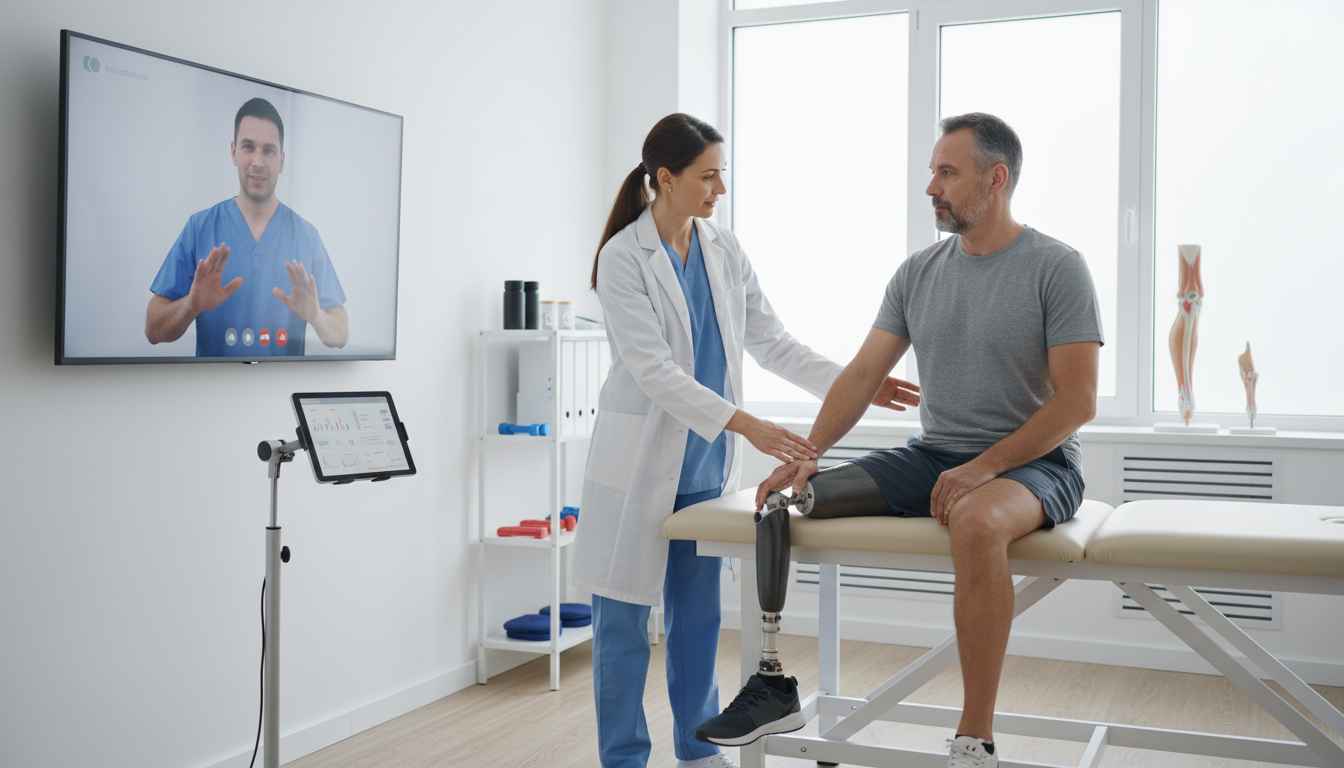
For physiotherapists working with patients post-amputation, the barriers to consistent care are a familiar frustration. Transportation difficulties, physical limitations, and geographical distance often hinder the frequency of clinic visits required for optimal functional recovery. With the acceleration of digital health solutions, telerehabilitation has emerged as a promising alternative. A significant Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT) published in Prosthetics and Orthotics International (February 2026) by Öztürk offers compelling evidence that remote care models can match, and in some metrics exceed, standard care expectations for lower limb amputees.
Study Design and Intervention Protocol
The study aimed to evaluate not only the physical improvements associated with telerehabilitation but also the psychological impact and patient adherence rates. The RCT recruited sixty participants with lower limb amputations, randomizing them into an experimental group (telerehabilitation) and a control group (standard care).
The intervention was structured into two distinct phases to mimic a tapering of clinical support:
- Phase 1 (Weeks 1-4): A supervised phase involving video-guided exercises.
- Phase 2 (Weeks 5-8): An unsupervised phase where patients continued the regimen independently.
Outcomes were measured using the Six-Minute Walk Test (6MWT) for physical capacity and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) for psychological status.
Significant Gains in Mobility and Mental Health
The results of this trial provide a strong argument for the integration of telehealth in orthopedic manipulation and rehabilitation. The experimental group demonstrated statistically significant improvements compared to the control group in both primary outcome measures.
Most notably, the mean distance covered in the 6MWT increased by 20% from baseline by the end of the supervised phase (P < 0.01). Crucially, these physical gains were maintained during the subsequent unsupervised phase, suggesting that the initial motor learning and strength adaptations established via video guidance were durable.
Psychologically, the intervention proved equally effective. Scores on the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale significantly decreased (P < 0.05). For lower limb amputees, who often face high rates of depression and body image anxiety, the ability to engage in effective rehabilitation from the privacy and comfort of home appears to offer a therapeutic mental health benefit.
The Adherence Challenge: Supervision Matters
While the physical and psychological outcomes are encouraging, the study highlights a critical nuance regarding patient engagement. During the supervised phase, adherence rates were robust at 85%. However, this dropped to 60% during the unsupervised phase.
For clinicians, this data point is vital. It suggests that while telerehabilitation is physically effective, the “human element” remains a driver of compliance. The drop in adherence during the unsupervised weeks indicates that hybrid models—where remote monitoring is continuous even if direct supervision is reduced—may be necessary to sustain long-term engagement.
Clinical Implications
This research validates telerehabilitation as more than just a convenience; it is a clinical tool that enhances functional capacity and mental well-being. Physiotherapists should consider implementing video-based protocols for amputees, particularly those with access barriers. However, successful implementation requires strategies to mitigate the “engagement drop-off” when moving to independent home programs.
References
Öztürk, B. (2026). Telerehabilitation transforms recovery: Elevating outcomes for lower limb amputees. Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 50(2). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41662536/